With growing environmental concerns, social consciousness, and awareness, the concept of corporate sustainability has evolved from a buzzword to a fundamental business strategy today. Beyond profit, companies are increasingly recognising the importance of their role in shaping a better future for both people and the planet.
Read on to learn about the significance of corporate sustainability, its key principles, benefits, and the transformative impact it can have on businesses and society.
Defining Corporate Sustainability
Corporate sustainability, also popularly referred to as corporate social responsibility (CSR) or sustainable business practices, is the integration of environmental, social, and ethical considerations into a company’s operations and decision-making processes. It goes beyond profit maximisation to encompass the broader impact of business activities on society and the environment.

Key Principles of Corporate Sustainability
Corporate sustainability is guided by several key principles that businesses should embrace:
- Environmental Stewardship: Sustainable businesses prioritise the responsible use of natural resources, reduce carbon emissions, and minimise waste and pollution.
- Social Responsibility: They commit to ethical labour practices, diversity and inclusion, and the well-being of employees, communities, and stakeholders.
- Economic Viability: Sustainability efforts should be economically viable, ensuring the financial health of the company in the long run.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparency in reporting sustainability efforts and being accountable for their impact are essential for building trust with stakeholders.

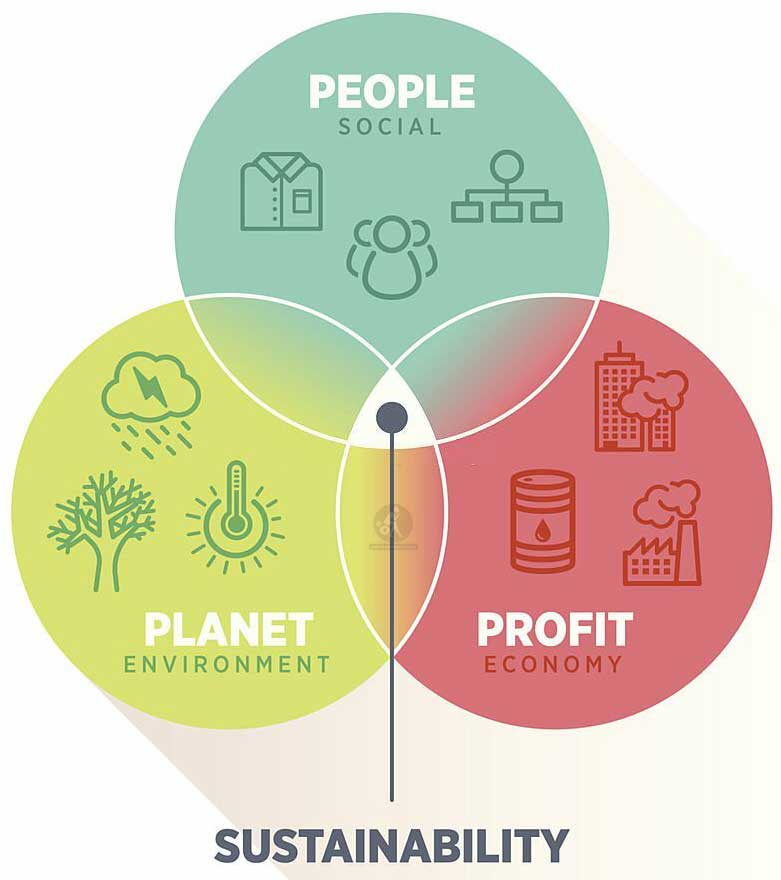
The Triple Bottom Line: People, Planet, Profit
One of the foundational concepts of corporate sustainability is the triple bottom line (TBL) framework. It emphasises that a company’s success should be measured not only by financial profit (the traditional bottom line) but also by its positive impact on people and the planet. Here’s a breakdown of the three ““P”s” in the TBL:
- People: Companies must consider the well-being of their people and the communities in which they operate. This involves fair labour practices, ethical supply chains, and community engagement.
- Planet: Environmental sustainability involves reducing the ecological footprint of business operations. This includes conserving resources, minimising pollution, and adopting sustainable practices.
- Profit: Profit remains a critical component, as it provides the financial stability necessary for a business to continue its sustainability efforts over the long term.
Benefits of Corporate Sustainability
Embracing corporate sustainability offers numerous advantages for businesses, society, and the environment:
- Enhanced Reputation: Companies that prioritise sustainability build trust with consumers and stakeholders, which can lead to increased brand loyalty and positive public perception.
- Cost Savings: Sustainability measures often result in reduced energy consumption, waste generation, and operational costs.
- Risk Mitigation: Sustainable practices can help companies mitigate risks associated with environmental regulations, supply chain disruptions, and reputation damage.
- Market Competitiveness: Sustainability can give businesses a competitive edge in a market increasingly focused on ethical and environmentally responsible products and services.
- Innovation: Sustainability encourages innovation, leading to the development of eco-friendly products and services that meet evolving consumer demands.
- Employee Engagement: Companies committed to sustainability tend to attract and retain top talent, as employees are often drawn to organisations that align with their values.

Challenges and Considerations
While corporate sustainability brings significant benefits, it also poses challenges and considerations:
- Initial Costs: Implementing sustainability initiatives may require upfront investments in technology, infrastructure, and employee training.
- Complex Supply Chains: Companies with global supply chains must ensure that sustainability practices extend throughout the entire chain, which can be complex and require collaboration with suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the landscape of environmental regulations and standards can be challenging, as regulations vary by region and change over time.
- Measuring Impact: Measuring the impact of sustainability efforts and demonstrating a return on investment can be difficult, but it’s essential for continued support and improvement.

A Sustainable Tomorrow
Corporate sustainability is not a passing trend; it is a fundamental shift in how businesses operate and contribute to society. Beyond profit, it embodies the idea that companies have a responsibility to impact the planet and the well-being of people positively.
By embracing corporate sustainability, businesses can not only thrive in a changing world but also help shape a better future for generations to come. It is a journey toward a more sustainable and prosperous tomorrow!